Backstage Scaffolder Parameters
Published on October 31st, 2024Parameters are how you get input data from users of Backstage Scaffolder templates. Parameters are defined in YAML alongside your template definition and rendered in a form when you run a template.
Here is the most basic example of a single parameter form field in a template:
---
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
name: parameters-example
spec:
owner: roadiehq
type: example
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
steps:
- id: log-message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello ${{ parameters.name }}'
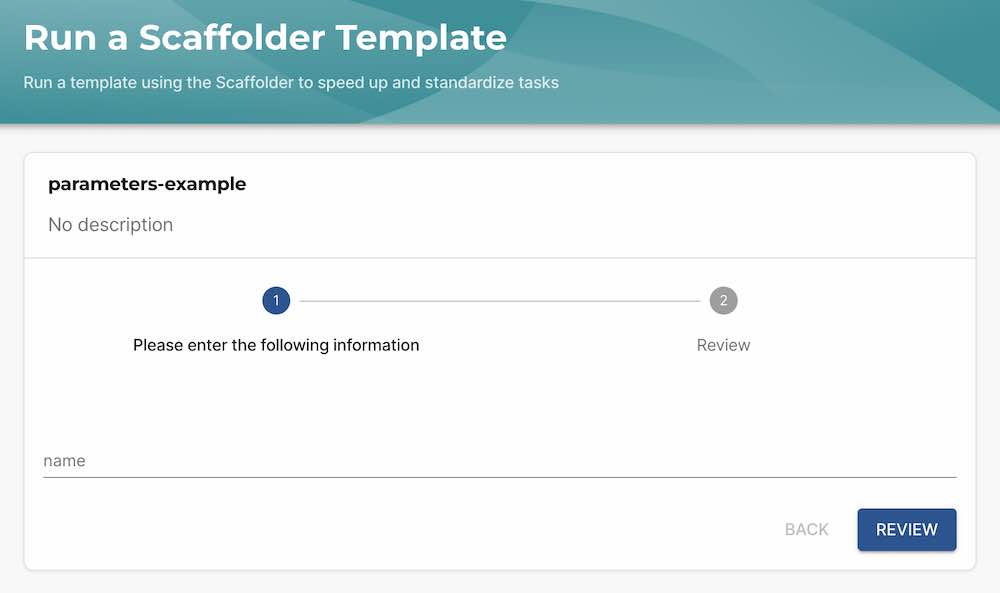
The parameters YAML is based on react-jsonschema-form . You can find the available base syntax options there and YAML examples here .
This page lists some examples from React Json Schema Form in YAML format for how to configure parameter forms in the Backstage Scaffolder.
Testing and iterating
You can test the core RJSF parameters live in Roadie at /create/tools -> Template Form Preview.
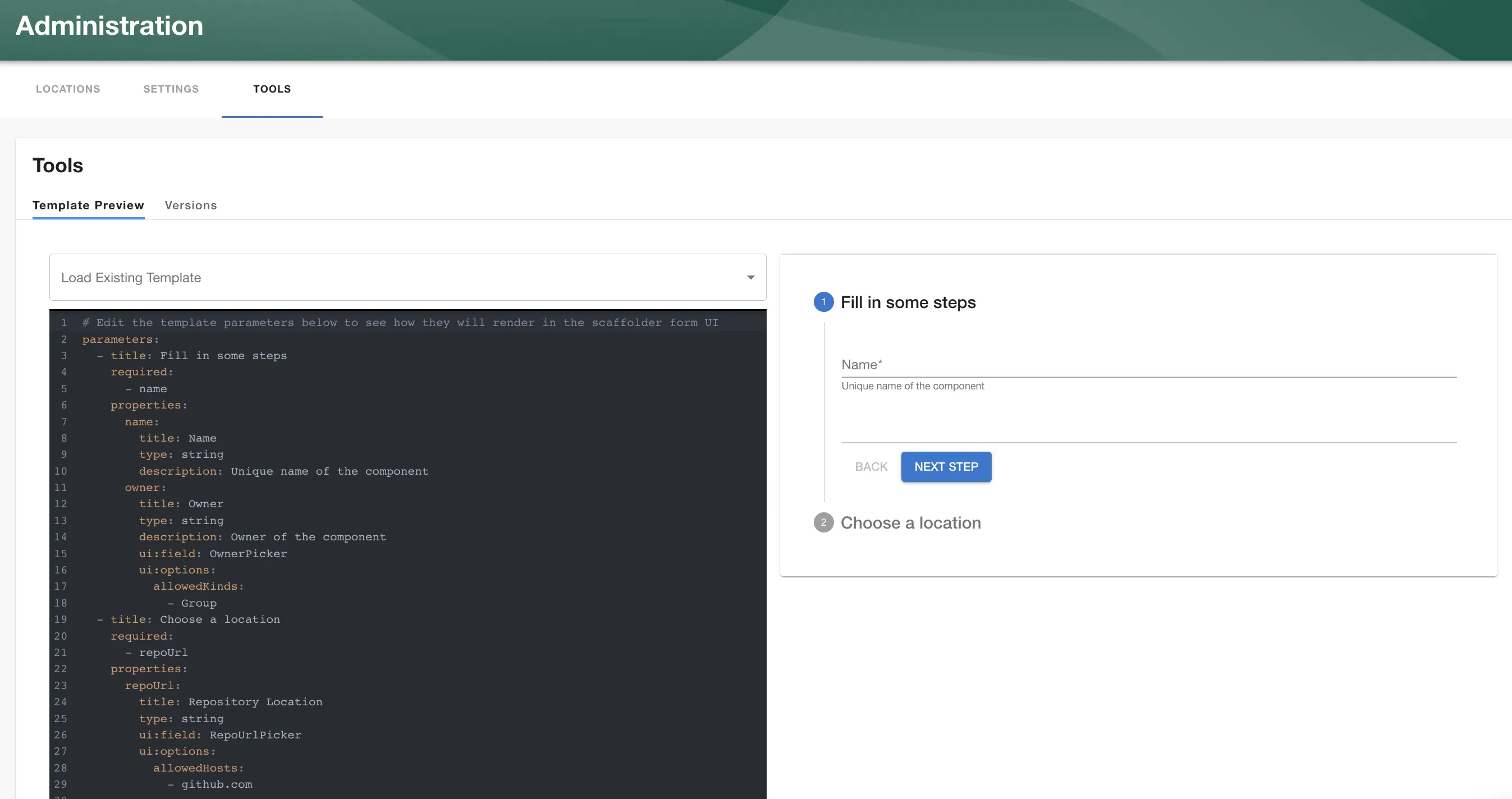
NB: This tool does not work with complex form fields and some syntax that will work in the real Scaffolder like a single page form structured as an object.
Field types
Each parameter can be one of a few types: string, number, array or object.
string
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
NB: You can validate strings using a regex with the pattern parameter. See Field Validation below.
number
You can allow the user to enter a number using the number type:
parameters:
properties:
size:
type: number
object
The object allows the collection of more complex types of data from the user. It contains the properties option to add variables to the object as follows:
parameters:
properties:
person:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string
age:
type: number
You may choose to make an object property to be mandatory using the required property.
parameters:
properties:
person:
type: object
required:
- name
properties:
name:
type: string
age:
type: number
array
You can prompt for an array of properties using the array option. The items option can be any type: array, object, string or number as you like.
parameters:
properties:
languages:
type: array
items:
type: string
enums
Enums values can be provided for all these types like so:
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
enum: ['Tom', 'Bob']
Enums render by default with a select dropdown.
Radio and Checkboxes
You can use a radio or checkbox by adding the widget field:
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
enum: ['Tom', 'Bob']
ui:widget: 'RadioWidget'
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
enum: ['Tom', 'Bob']
ui:widget: 'CheckboxesWidget'
Multi select
Multi select can be achieved using the array type:
properties:
names:
title: Names
type: array
ui:widget: 'CheckboxesWidget'
uniqueItems: true
items:
enum:
- Tom
- Bob
Enum Display Names
You can render a different name for your enum values using enumNames:
properties:
city:
title: City
type: string
enumNames:
- New York
- Amsterdam
- Hong Kong
enum:
- nyc
- ams
- hk
This is particularly useful for encoding additional hidden data in your enum values that can be used in later template steps:
properties:
city:
title: City
type: string
enumNames:
- New York
- Amsterdam
- Hong Kong
enum:
- name: 'New York'
lat: 40
lon: 74
- name: Amsterdam
lat: 52
lon: 5
- name: 'Hong Kong'
lat: 22
lon: 114
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'The city ${{ parameters.city.name }} is at ${{ parameters.city.lat }},${{ parameters.city.lon }}'
Field Validation
You can use react-jsonschema-form to perform validation on input fields using a regex in the pattern filed or character counts using maxLength and minLength.
parameters:
properties:
name:
title: Simple text input
type: string
description: Description about input
maxLength: 8
pattern: '^([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*)(-[a-zA-Z0-9]+)*$'
ui:autofocus: true
ui:help: 'Hint: additional description...'
errorMessage:
properties:
name: '1-8 alphanumeric tokens (first starts with letter) delimited by -'
Multi Page Forms
You can choose to break up the parameters into form pages or collect all the parameters in one single page.
Single Page:
parameters:
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
email:
title: Email
type: string
maxLength: 8
pattern: '^[^\s@]+@([^\s@.,]+\.)+[^\s@.,]{2,}$'
role:
title: Role
type: string
company:
title: Company Name
type: string
Multi Page:
parameters:
- title: Provide some info about yourself
required:
- name
- email
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
email:
title: Email
type: string
maxLength: 8
pattern: '^[^\s@]+@([^\s@.,]+\.)+[^\s@.,]{2,}$'
- title: Provide some info about your occupation
properties:
role:
title: Role
type: string
company:
title: Company Name
type: string
In a multipage form, each parameter page must contain title and properties
Complex Form Fields (Builtin Custom Fields)
The following items are enhanced form fields that can be used out of the box to build richer forms for your templates.
Roadie allows you to create your own custom React form components and use them in the same way if you have special use cases.
Entity picker
You can prompt the user with a list of catalog entities using the ui:field: EntityPicker option as follows:
parameters:
properties:
entity:
type: string
ui:field: EntityPicker
Owned entity picker
Alternatively if you would like the user to only select entities that they already own, you might want to use the OwnedEntityPicker.
parameters:
properties:
ownedEntity:
type: string
ui:field: OwnedEntityPicker
Entity name picker
If you would like a little validation when the user enters an Entity name, you can use the EntityNamePicker. It will prevent the user from entering an entity name that is not an acceptable entity name.
parameters:
properties:
ownedEntity:
type: string
ui:field: EntityNamePicker
Repository picker
The respository picker can allow the user to select the name and location of a new repository. The picker restricts the target location of the repository to make it a little easier for the user to select a target location.
The following example, will only allow the user to enter a new repository name targeting the GitHub using the AcmeInc organization.
parameters:
properties:
repoUrl:
type: string
ui:field: RepoUrlPicker
ui:options:
allowedHosts:
- github.com
allowedOwners:
- AcmeInc
The RepoUrlPicker uses the allowedHosts to decide how to build the repo url output value. If you use bitbucket.org it will output a valid repo url for Bitbucket.
parameters:
properties:
repoUrl:
type: string
ui:field: RepoUrlPicker
ui:options:
allowedHosts:
- bitbucket.org
Owner picker
The owner picker, allows the user to select a user / group in the Backstage catalog. e.g.
parameters:
properties:
owner:
type: string
ui:field: OwnerPicker
This returns a variable in the format group:<namespace>/<group-or-user-name>. You can extract the entity name using replace when you refer to the parameter like so: ${{ parameters.owner | replace(\"group:.*/\", \"\") }}
Picker from external API source
This custom scaffolder field, makes an API call to the Backstage backend and allows the result to be rendered to a list.
labelSelector and labelTemplate are mutually exclusive and cannot both be used in a single property field.
parameters:
- title: Fill in some steps
properties:
custom:
title: Custom
type: string
description: Custom field from external API
# Use `SelectFieldFromApi` to configure the select field for the entry.
ui:field: SelectFieldFromApi
ui:options:
# The Path on the Backstage API and the parameters to fetch the data for the dropdown
path: catalog/entity-facets
params:
facet: kind
# This selects the array element from the API fetch response. It finds the array with the name kind
# under the facets object
arraySelector: facets.kind
# (Optional) This selects the field in the array to use for the value of each select item. If its not specified
# it will use the value of the item directly.
valueSelector: count
# (Optional) This selects the field in the array to use for the label of each select item.
labelSelector: 'value'
# (Optional) This selects the fields in the array to use for the label of each select item with Nunjucks templating format.
labelTemplate: '{{ item.value }}:{{ item.count }}'
Some of the SelectFieldFromApi options allow using parameters from earlier parameter pages to be used to template the options. The templated options are params, path, valueSelector and labelSelector. e.g.
parameters:
- title: Select an Entity kind
required:
- kind
properties:
kind:
title: Kind
type: string
enum:
- template
- location
default: template
ui:autofocus: true
ui:options:
rows: 5
- title: Select the specific entity you want
properties:
obj:
title: custom
type: string
description: Entity Selector
ui:field: SelectFieldFromApi
ui:options:
path: 'catalog/entities'
params:
filter: 'kind={{ parameters.kind }}'
valueSelector: 'metadata.name'
labelSelector: 'metadata.description'
Searchable picker from external API source
This custom scaffolder field renders a searchable dropdown and fetches results from the Backstage backend with pagination, making it better suited for large datasets.
parameters:
properties:
ec2Instance:
type: string
# Use `SearchableSelectApi` to configure the searchable select field.
ui:field: SearchableSelectApi
ui:options:
# Path on the Backstage API and parameters to fetch the data for the dropdown
path: /catalog/entities/by-query
params:
filter: kind=Resource,spec.type=ec2-instance
# This selects the array element from the API fetch response.
arraySelector: items
# This selects the fields to use for the value and label of each select item.
valueSelector: metadata.name
labelSelector: metadata.title
# Optional UI text
title: EC2 Instance
placeholder: Search instances...
Integration and Plugin specific parameters
GitOps Manifest Updater (Crossplane)
This parameter field takes no input and only supports Crossplane manifest files at this time.
The GitOps Manifest Updater field extension allows you to update Kubernetes manifests stored in Git repositories directly from your Backstage templates. It automatically generates forms based on the OpenAPI schema of Kubernetes CRDs, letting you update GitOps-managed resources with a user-friendly interface.
parameters:
properties:
manifest:
title: Update GitOps Manifest
type: string
description: Update Kubernetes manifest in Git repository
ui:field: GitOpsManifestUpdater
ui:options:
# You can either use an entity annotation to provide the manifest URL
# or allow the user to input it directly in the form
manifestSourceType: 'entityAnnotation' # or "manualInput"
# If using entityAnnotation, specify which annotation contains the URL
sourceAnnotation: 'terasky.backstage.io/source-manifest-url'
# Alternatively, provide a default URL when using manualInput
defaultManifestUrl: 'https://github.com/example/repo/path/to/manifest.yaml'
You can find a full example here
This field extension is particularly useful for:
- Updating Crossplane claims and other Kubernetes CRDs stored in Git repositories
- Implementing day-2 operations for GitOps-managed resources
- Creating pull requests to modify existing Kubernetes manifests with schema validation
The plugin generates a dynamic form based on the OpenAPI schema of the resource, populates it with current values from the Git repository, and creates a PR with the changes when submitted.
Adding custom parameters
You can extend and customize the available Scaffolder functionality by using Roadie Custom Plugins and creating a Field extension.
You can find more information on how this is done in the tutorial on the Open Source Backstage documentation page.
Field extensions are react form components that can be imported dynamically into the Roadie Scaffolder. You can use the same workflow and development experience to build your own custom Scaffolder Field Extensions as any other plugin, using the Roadie CLI.
Registering your Field Extension
Scaffolder Field Extensions are automatically registered to be usable within Scaffolder Templates, once they have been registered as a Custom Plugin component in the Roadie application. You can do this by navigating to the Administration -> Custom Plugins page and registering your Custom Plugin bundle, including a component of type ScaffolderFieldExtension.
Re-using Parameter Pages
You can create re-usable form pages using the placeholders feature like so:
---
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
name: global-param-example
title: Example of sourcing params from a constant
spec:
owner: roadie
type: service
parameters:
- $yaml: ./constants/products.yaml
steps:
- id: log-message
name: List selected product
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Selected product: ${{ parameters.product }}'
./constants/products.yaml
title: Select Product
properties:
product:
title: Product
type: string
enum: ['Search', 'CRM', 'Onboarding']
NB: This only works for top level parameters objects and not for sections within a form page.
Using Parameters In Actions
Parameters can be retrieved later on by action steps using parameter outputs. Here is an example of a parameter name being used by a debug:log step.
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.name }}!'
If you need to reference elements of an array parameter you can refer to them using the following syntax:
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.names[0] }}!'
An object parameter values can be reference in the way you might expect. Keys with special characters can be accessed via square bracket notation like so ${{ parameters["something-else"] }}
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.person.name }}!'
Using logic in Parameter references
Inliine logic can be used in these references also via pipe functions using Nunjucks templating syntax .
i.e.
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: "Hello, ${{ parameters.name | replace('Mr', 'Mrs') | capitalize }}! You have lived at the following addresses: ${{ parameters.addresses | join(", ") }}"
Available filters are listed in Nunjucks documentation here .
Default values
If you would like to default the value of a field you can use the default option:
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
default: 'world!'
Field display options
You can display a more human description to a field value by using title and description
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
title: 'Name'
description: 'Name to say hello to'
Links
- [React Json Schema Form](https://rjsf-team.github.io/react-jsonschema-form/
- Official Backstage docs .
- Nunjucks templating docs